Inside a Modern Light Weight Aluminum Shop: What Happens From Thawing to Final Evaluation
Inside a modern light weight aluminum foundry, the change of raw materials into completed items is a complex and systematic process. Each stage, from selecting the right alloys to final inspections, plays a vital function. Knowledgeable operators and progressed innovation work in consistency to ensure top quality and accuracy. As the journey unfolds, the complex steps reveal the meticulous care taken to fulfill market standards. What developments and obstacles await in this crucial production domain name?
The Raw Products: Comprehending Light Weight Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys work as the structure for the modern-day aluminum foundry procedure, supplying a versatile series of homes customized for various applications. These alloys are primarily made up of light weight aluminum, with other components like copper, silicon, zinc, and magnesium included to enhance certain attributes. Each alloying aspect adds special qualities, such as raised toughness, boosted corrosion resistance, or boosted machinability.
The category of aluminum alloys is commonly divided into two groups: wrought and cast. Wrought alloys are refined through mechanical methods, while cast alloys are developed by pouring liquified metal right into molds. The choice of alloy depends upon the planned usage, with some alloys enhanced for high-performance aerospace components, while others are suited for automotive applications. Understanding the structure and features of these alloys is necessary for makers to meet the strict needs of contemporary engineering and design needs.
Thawing Process: Transforming Solid to Fluid
The melting procedure is a crucial step in the light weight aluminum factory, where strong aluminum alloys are changed into a fluid state to assist in spreading. This improvement begins with the mindful choice of basic materials, complied with by their placement in a furnace made to attain heats. Shops usually make use of either induction or reverberatory heaters, each offering distinctive benefits for melting effectiveness and energy usage.
As the strong light weight aluminum heats, it undergoes a stage adjustment, with the temperature very closely kept an eye on to guarantee even melting. Oxides and contaminations are usually eliminated during this stage, enhancing the high quality of the liquified light weight aluminum. The process requires skilled operators that take care of the heater problems, making certain the alloy gets to the preferred temperature and structure. Once the aluminum is completely melted, it awaits the next stage, allowing exact spreading that satisfies rigorous market requirements.
Putting Techniques: Precision in Every Decrease
Pouring liquified aluminum right into molds needs precise precision to assure that each drop fills the tooth cavity evenly and precisely. Numerous methods are employed to attain this degree of accuracy, with each approach tailored to certain casting demands. The pouring process is frequently guided by the use sophisticated equipment, such as automated pouring systems, which guarantee consistent circulation prices and temperature levels.
Furthermore, operators monitor the thickness of the liquified aluminum, as variations can considerably impact how well the steel loads intricate mold and mildew styles. Aluminum Foundry. The angle and height where the aluminum is put are additionally important variables; improper putting can bring about defects such as air pockets or incomplete fills
To reduce these threats, proficient technicians utilize practice and experience, adjusting their methods based upon real-time comments. Overall, the mix of advanced innovation and human expertise is necessary for achieving perfect pouring cause modern aluminum foundries.
Molding Approaches: Shaping the Future
Molding techniques play a crucial function in the aluminum foundry process, affecting both quality and effectiveness. Amongst the primary techniques are sand spreading and die spreading, each offering distinct advantages for different applications. Recognizing these methods is essential for shaping the future of light weight aluminum production.
Sand Casting Strategies
Sand casting has been a basic strategy in metalworking for centuries, its innovative applications proceed to develop, shaping the future of the light weight aluminum factory procedure. This versatile method includes developing mold and mildews from sand, which can be quickly shaped and reused, making it cost-effective for large production. Modern developments have boosted the accuracy and efficiency of sand casting, enabling for complicated geometries and lowered lead times. Techniques such as chilly box and no-bake sand spreading are getting appeal because of their ability to generate top notch mold and mildews with improved surface coatings. Additionally, the combination of computer-aided layout (CAD) and simulation software application facilitates maximized mold design, additionally refining the spreading process and making certain constant quality in light weight aluminum components.
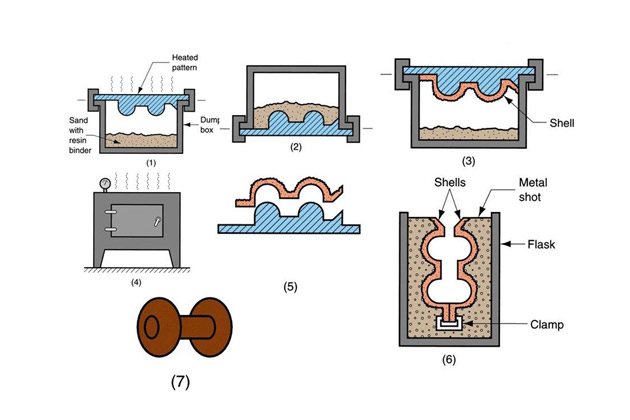
Die Casting Processes

Air conditioning and Solidification: From Liquid to Solid
The shift from fluid to solid in the light weight aluminum factory process is a crucial phase that greatly affects the final residential or commercial properties of the cast product - Precision aluminum casting. Once the liquified light weight aluminum is poured into mold and mildews, it starts to shed heat, launching the cooling process. The temperature decrease triggers the light weight aluminum atoms to shed power and arrange themselves right into a solid latticework structure. This change why not try these out occurs at specific temperatures, referred to as the solidification variety, which varies relying on the alloy structure
Air conditioning prices play a considerable role; rapid cooling can result in finer microstructures, boosting strength, while slower cooling may result in coarser grains and explanation reduced mechanical buildings. In addition, the layout of the mold and the density of the spreadings impact cooling down rates. Appropriate control of these parameters assurances consistent solidification, minimizing issues such as porosity or bending. This stage inevitably establishes the stability and performance of the ended up aluminum part.
Finishing Processes: Attaining Excellence
The ending up procedures in aluminum factory procedures play an essential duty in improving the last product's look and efficiency. Surface area treatment strategies, such as anodizing and polishing, are important for attaining preferred practical and aesthetic qualities. Additionally, executing stringent high quality control measures ensures that each component fulfills market requirements and requirements.
Surface Treatment Techniques
While achieving a perfect surface in light weight aluminum foundry procedures is critical, the option of appropriate surface area therapy methods plays a crucial duty. Various techniques are used to improve the appearance, corrosion, and durability resistance of light weight aluminum parts. Anodizing, for circumstances, includes developing a protective oxide layer that increases resistance to use and improves visual appeal. An additional strategy is powder finishing, which not only offers a durable finish however likewise permits a variety of textures and shades. In addition, chemical polishing can be used to accomplish a brilliant, reflective surface. Each of these treatments offers to improve the total high quality and durability of the finished product, guaranteeing that elements fulfill the rigid needs of their desired applications.
Quality Assurance Procedures
Ensuring the finest in light weight aluminum factory processes demands rigorous quality assurance steps throughout the ending up phases. These procedures include thorough assessments at each production phase, where trained personnel examine surface honesty click here for info and dimensional accuracy. Advanced techniques such as non-destructive screening (NDT) are employed to discover possible problems without jeopardizing the product's framework. Additionally, chemical evaluation is carried out to confirm the alloy composition, ensuring it fulfills specified standards - Aluminum Foundry. Tracking equipment calibrations and keeping accurate temperature controls during procedures like plating even more improve high quality. Last inspections include evaluating visual elements, such as surface coating and shade uniformity. By implementing these extensive quality assurance measures, factories can ensure customers of the integrity and toughness of their aluminum products
Quality Control: Making Certain Standards Are Met
Quality control plays a crucial role in the aluminum shop process, as it straight influences product stability and performance. Each stage of manufacturing is diligently kept track of to ensure conformity with market requirements and requirements. This starts with basic material assessment, where the top quality of aluminum ingots is validated for pureness and structure. Throughout the melting phase, temperature level and alloy ratios are carefully regulated to achieve perfect outcomes.
As liquified light weight aluminum is put right into mold and mildews, technicians perform aesthetic assessments to identify any type of problems, such as air bubbles or imbalances. After cooling down, castings undertake dimensional checks making use of specific measuring tools to verify they meet called for resistances.
Finally, completed products are subjected to extensive screening, including mechanical and chemical evaluations, to validate their durability and efficiency capabilities. This detailed quality assurance procedure guarantees that each component not just fulfills yet exceeds consumer assumptions, enhancing the factory's track record for quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Precaution Are Executed in an Aluminum Foundry?
Precaution in a light weight aluminum foundry consist of protective equipment, air flow systems, fire suppression devices, routine security training, danger communication, and strict adherence to procedures to stop crashes and ensure the wellness of all workers.
Just How Is Waste Managed During the Light Weight Aluminum Spreading Process?
Waste management throughout the aluminum casting procedure involves recycling scrap aluminum, correctly getting rid of hazardous materials, and using dust collection systems. These steps aid decrease environmental influence while guaranteeing reliable source use throughout manufacturing.
What Kinds of Machinery Are Used in Modern Foundries?
How Are Light Weight Aluminum Alloys Selected for Specific Applications?
Light weight aluminum alloys are chosen based on mechanical residential properties, rust resistance, thermal conductivity, and weight needs. Engineers assess application demands, conducting analyses and tests to guarantee peak efficiency and compatibility with the meant use the end product.

What Qualifications Do Factories Need to Operate Lawfully?
Foundries should obtain various accreditations to operate legally, consisting of ISO, ASTM, and industry-specific criteria. These accreditations assure compliance with safety and security policies, quality control, and environmental management, advertising trust fund among clients and adherence to lawful demands.
Aluminum alloys serve as the structure for the modern-day light weight aluminum shop process, offering a flexible variety of residential properties customized for different applications. The melting process is an important action in the aluminum shop, where strong aluminum alloys are changed into a liquid state to help with spreading. Sand spreading has been a fundamental method in metalworking for centuries, its innovative applications continue to evolve, forming the future of the light weight aluminum foundry process. Ensuring the greatest top quality in light weight aluminum factory processes necessitates strenuous quality control steps throughout the finishing phases. Waste monitoring throughout the light weight aluminum spreading procedure includes reusing scrap aluminum, properly disposing of hazardous materials, and using dirt collection systems.